Aniruddh Nayak's Heavenly Photos
When Ani said that he was willing to email some of his photos to me and that I could place them on my webpage, I was so very humbly honored. We are blessed to have Ani & his wife Veda to be our neighbors here in HW.
I am hoping that Ani can share some stories about when, where, how, who he was with, and other stories associated with each of his photos below. Possibly, future cloudy day Stargazer opportunities if Ani is present. Enjoy Ani's professionally taken photos below as you can learn a lot about our night sky by researching each of these photos.
Note that I had to start placing Ani's photos in categories so enjoy scrolling though the categories.
I am hoping that Ani can share some stories about when, where, how, who he was with, and other stories associated with each of his photos below. Possibly, future cloudy day Stargazer opportunities if Ani is present. Enjoy Ani's professionally taken photos below as you can learn a lot about our night sky by researching each of these photos.
Note that I had to start placing Ani's photos in categories so enjoy scrolling though the categories.
Galaxies
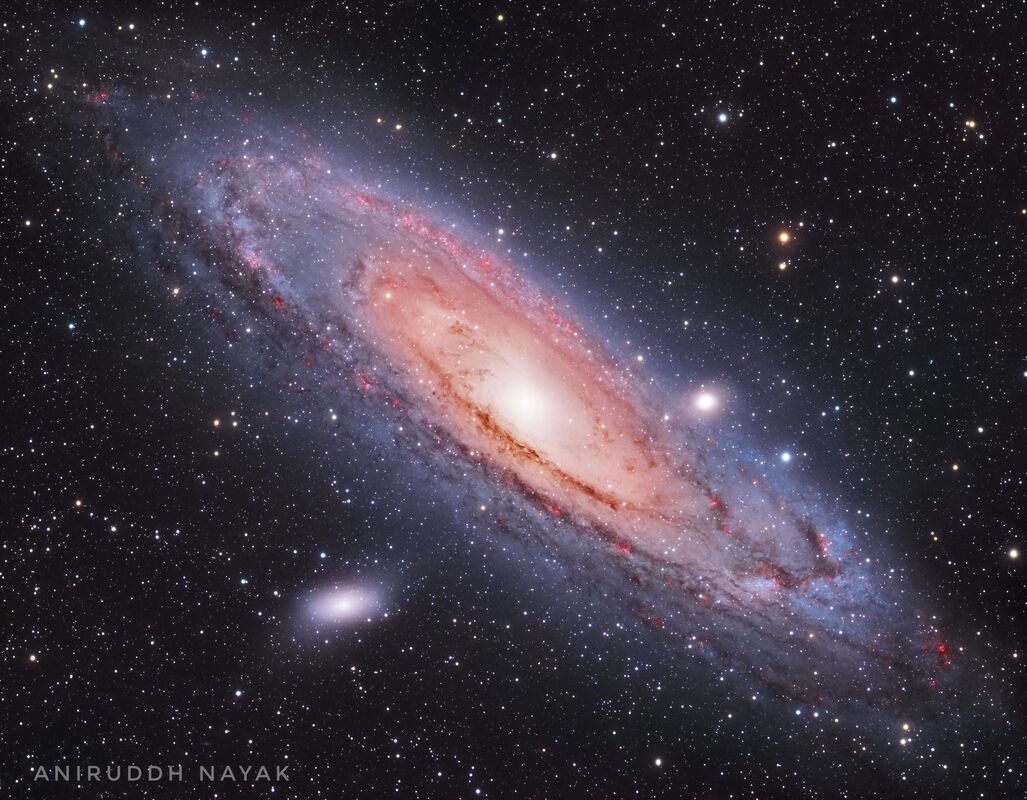

The Andromeda Galaxy
Designation: M31 or NGC 224
Type: Spiral Galaxy (Milky Way is a Barred Spiral)
Diameter: 220,000 LY (Milky Way Galaxy's diameter is 100,000 LY)
Distance from our Milky Way: 2.54 million LY
# of stars: 1 trillion (Milky Way Galaxy has 100-400 billion stars as it is hard to tell because we live in it.)
Constellation: Andromeda (Milky Way is in Sagittarius)
Group: Local (Milky Way is the 2nd largest galaxy in the Local Group where Andromeda is the largest)
Type: Spiral Galaxy (Milky Way is a Barred Spiral)
Diameter: 220,000 LY (Milky Way Galaxy's diameter is 100,000 LY)
Distance from our Milky Way: 2.54 million LY
# of stars: 1 trillion (Milky Way Galaxy has 100-400 billion stars as it is hard to tell because we live in it.)
Constellation: Andromeda (Milky Way is in Sagittarius)
Group: Local (Milky Way is the 2nd largest galaxy in the Local Group where Andromeda is the largest)
The Andromeda Galaxy (M31) is the closest large galaxy to the Milky Way and is one of a few galaxies that can be seen unaided from the Earth. In approximately 4.5 billion years the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way are expected to collide and the result will be a giant elliptical galaxy. Andromeda is accompanied by 14 dwarf galaxies, including M32, M110, and possibly M33 (The Triangulum Galaxy).
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way. It has a total diameter of roughly 3 megaparsecs (10 million light-years; 9×1022 metres),[1] and a total mass of the order of 2×1012 solar masses (4×1042 kg).[2] It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about 800 kpc (3×106 ly; 2×1022 m) and are moving toward one another with a velocity of 123 km/s.[3] The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies.
The two largest members, the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way, are both spiral galaxies with masses of about 1012 solar masses each. Each has its own system of satellite galaxies:
The two largest members, the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way, are both spiral galaxies with masses of about 1012 solar masses each. Each has its own system of satellite galaxies:
- The Andromeda Galaxy's satellite system consists of Messier 32 (M32), Messier 110 (M110), NGC 147, NGC 185, Andromeda I (And I), And II, And III, And V, And VI (also known as the Pegasus Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy, or Pegasus dSph), And VII (also known as the Cassiopeia Dwarf Galaxy), And VIII, And IX, And X, And XI, And XIX, And XXI and And XXII, plus several additional ultra-faint dwarf spheroidal galaxies.[4]
- The Milky Way's satellite galaxies system comprises the Sagittarius Dwarf Galaxy, Large Magellanic Cloud, Small Magellanic Cloud, Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy (disputed, considered by some not a galaxy), Ursa Minor Dwarf Galaxy, Draco Dwarf Galaxy, Carina Dwarf Galaxy, Sextans Dwarf Galaxy, Sculptor Dwarf Galaxy, Fornax Dwarf Galaxy, Leo I (a dwarf galaxy), Leo II (a dwarf galaxy), Ursa Major I Dwarf Galaxy and Ursa Major II Dwarf Galaxy, plus several additional ultra-faint dwarf spheroidal galaxies.[5]
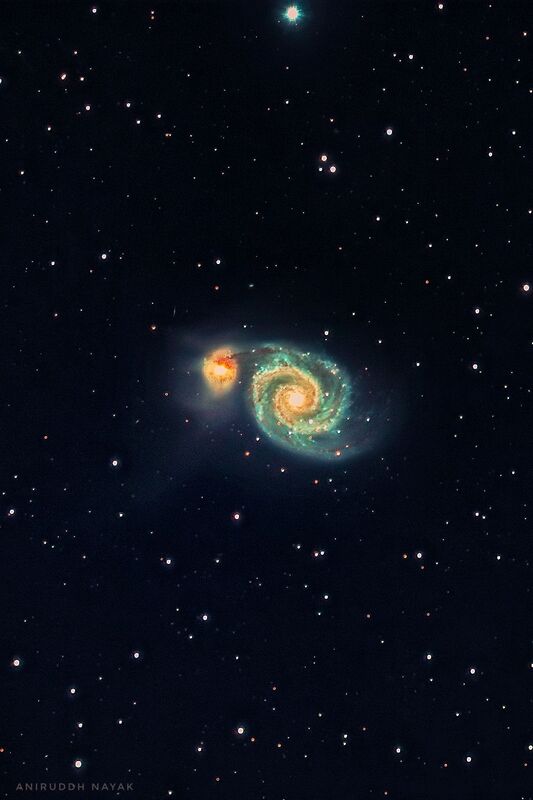
The Whirlpool Galaxy
Designation: M51a or NGC 5194
Type: Interacting Grand-Design Spiral Galaxy
Constellation: Canes Venatici
Galactic Group: M51 Group
Distance from Earth: 31 million LY
Type: Interacting Grand-Design Spiral Galaxy
Constellation: Canes Venatici
Galactic Group: M51 Group
Distance from Earth: 31 million LY
Nebula
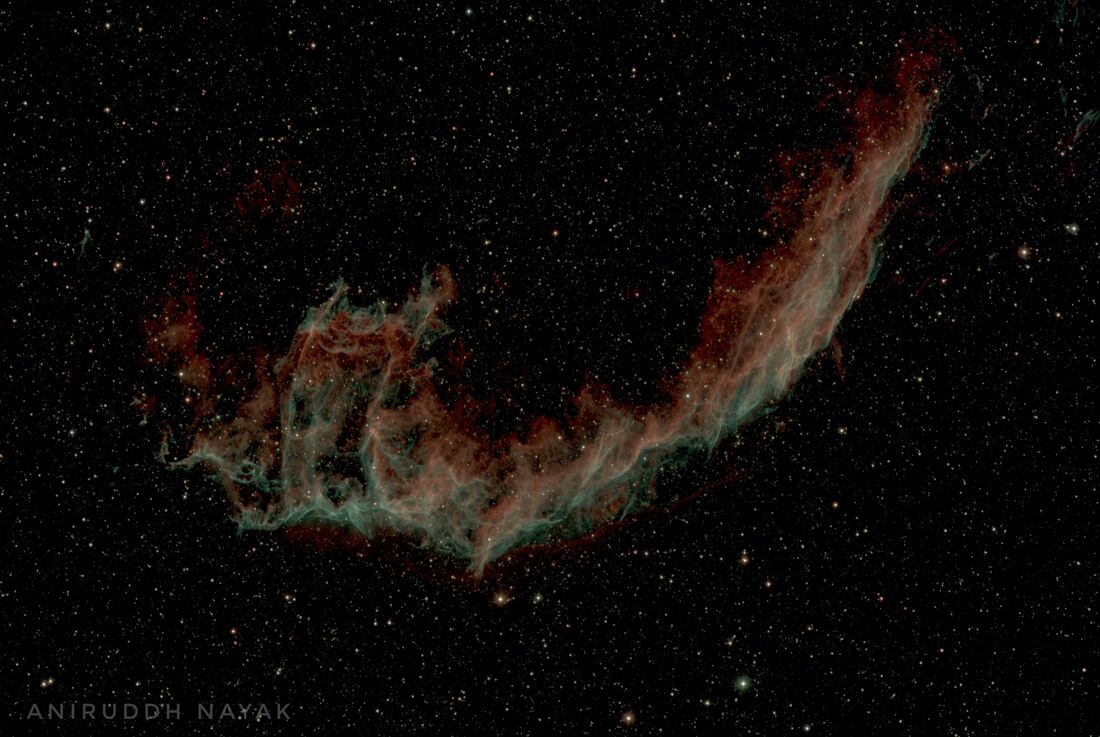
Veil Nebula
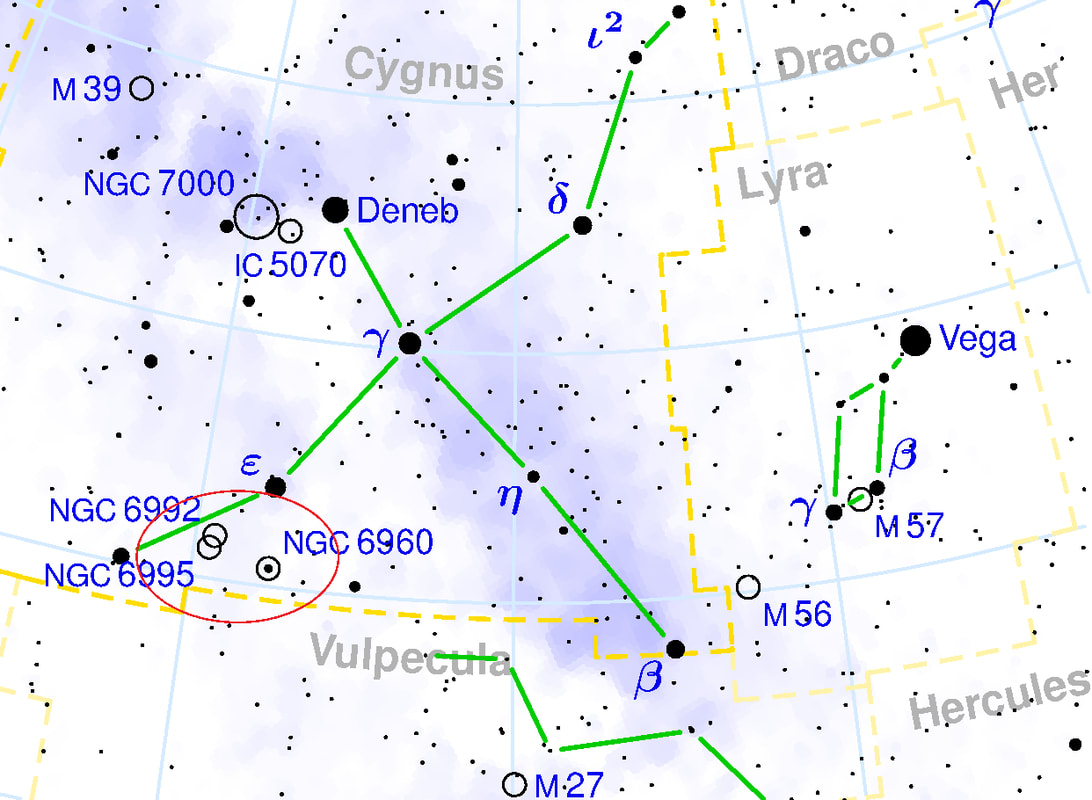
The Veil Nebula is a diffuse nebula located in the northern constellation Cygnus, the Swan. Also known as Witch’s Broom Nebula, Bridal Veil Nebula, Cirrus Nebula, or Filamentary Nebula, it constitutes the visible parts of the Cygnus Loop, a supernova remnant in Cygnus. It is located at an approximate distance of 1,470 light years from Earth.
The Veil Nebula has three main parts: the Eastern Veil, the Western Veil, and Fleming’s Triangle (Pickering’s Triangle). It has the designations NGC 6960, NGC 6992, NGC 6995, NGC 6974, and NGC 6979 in the New General Catalogue, and the southernmost part of the Eastern Veil Nebula was assigned the catalogue designation IC 1340.
The Veil Nebula has three main parts: the Eastern Veil, the Western Veil, and Fleming’s Triangle (Pickering’s Triangle). It has the designations NGC 6960, NGC 6992, NGC 6995, NGC 6974, and NGC 6979 in the New General Catalogue, and the southernmost part of the Eastern Veil Nebula was assigned the catalogue designation IC 1340.
The Pelican Nebula

The Pelican Nebula is an emission nebula located near the bright star Deneb in the constellation Cygnus, the Swan. Named for its resemblance to a pelican, the nebula is associated with the neighbouring North America Nebula (NGC 7000) and is one of several notable nebulae found in the area of the Northern Cross. It is an active star forming region with a particularly active mix of star formation and evolving gas clouds.
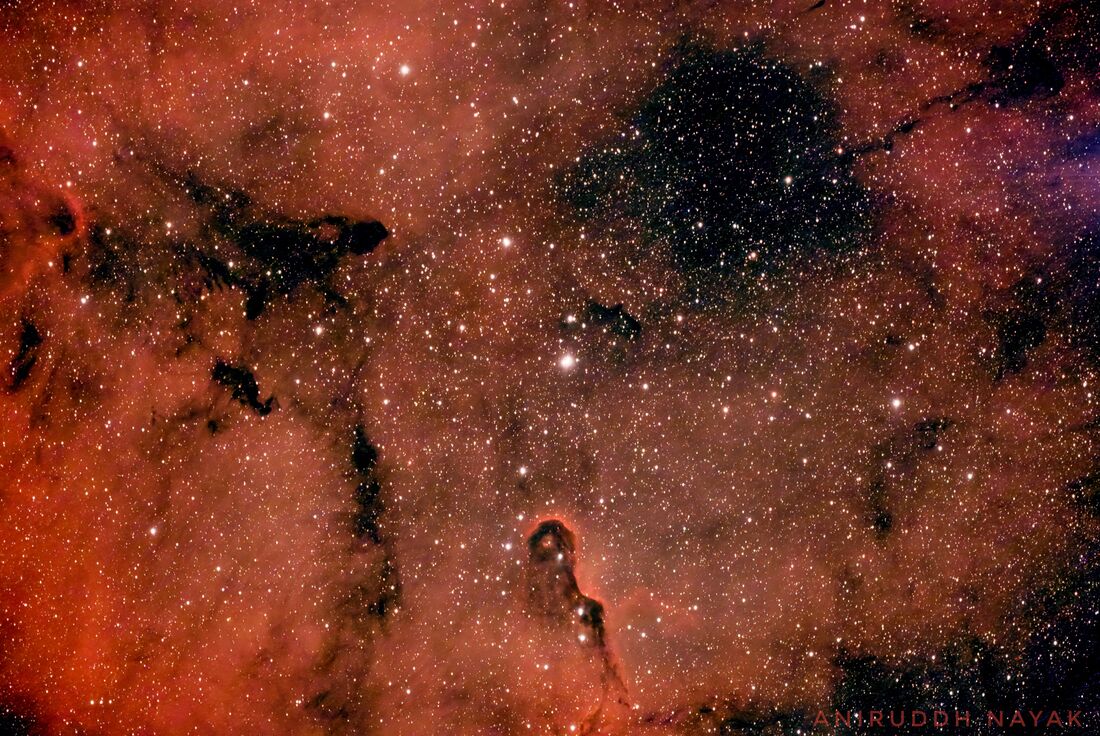
Elephant Trunk Nebula
The Elephant’s Trunk Nebula is a dense region of dust and gas found within the considerably larger star forming region IC 1396 in Cepheus constellation. Designated IC 1396A, the elongated globule of dust and gas was named the Elephant’s Trunk because it resembles an elephant’s head and trunk at visible wavelengths, appearing as a dark patch with a bright winding rim. It is located at a distance of 2,400 light years from Earth.
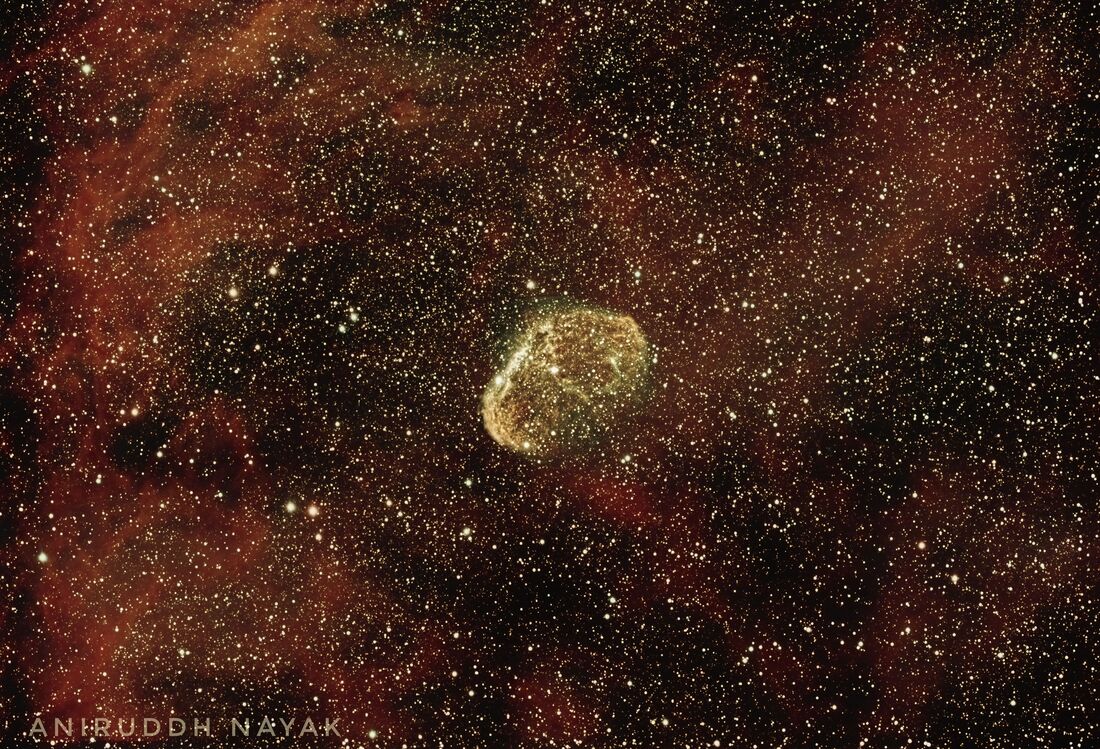
Crescent Nebula
The Crescent Nebula (also known as NGC 6888, Caldwell 27, Sharpless 105) is an emission nebula in the constellation Cygnus, about 5000 light-years away from Earth. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1792.[2] It is formed by the fast stellar wind from the Wolf-Rayet star WR 136 (HD 192163) colliding with and energizing the slower moving wind ejected by the star when it became a red giant around 250,000[3] to 400,000[citation needed] years ago. The result of the collision is a shell and two shock waves, one moving outward and one moving inward. The inward moving shock wave heats the stellar wind to X-ray-emitting temperatures.
It is a rather faint object located about 2 degrees SW of Sadr. For most telescopes it requires a UHC or OIII filter to see. Under favorable circumstances a telescope as small as 8 cm (with filter) can see its nebulosity. Larger telescopes (20 cm or more) reveal the crescent or a Euro sign shape which makes some to call it the "Euro sign nebula".
It is a rather faint object located about 2 degrees SW of Sadr. For most telescopes it requires a UHC or OIII filter to see. Under favorable circumstances a telescope as small as 8 cm (with filter) can see its nebulosity. Larger telescopes (20 cm or more) reveal the crescent or a Euro sign shape which makes some to call it the "Euro sign nebula".
Star Clusters
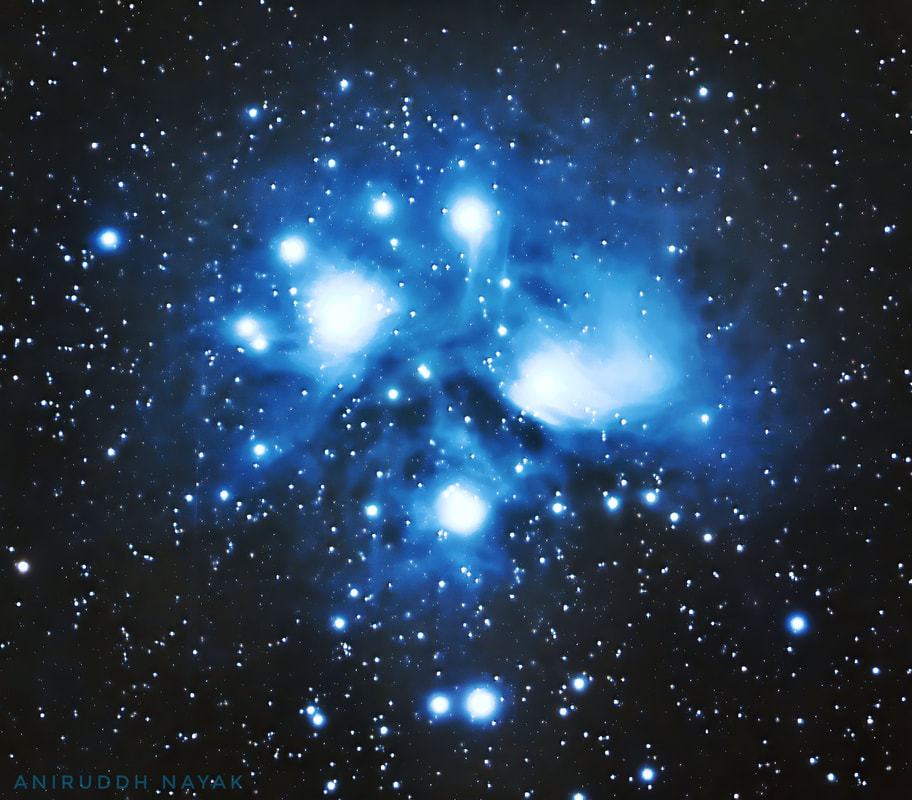
Pleiades Star Cluster
Key Facts & Summary of the Pleiades Star Cluster or The Seven Sisters Star Cluster
- The Pleiades open star cluster is located in the zodiacal constellation of Taurus, the celestial bull, at around 444 light-years / 136 parsecs away from the Sun.
- The Pleiades is among the nearest star clusters to Earth, and it is also visible to the naked eye.
- Both the constellation of Taurus and the Pleiades were known to the ancients, and many myths and legends were associated with them.
- The Pleiades open cluster is dominated by hot blue and luminous stars that have formed between 75 to 150 million years ago.
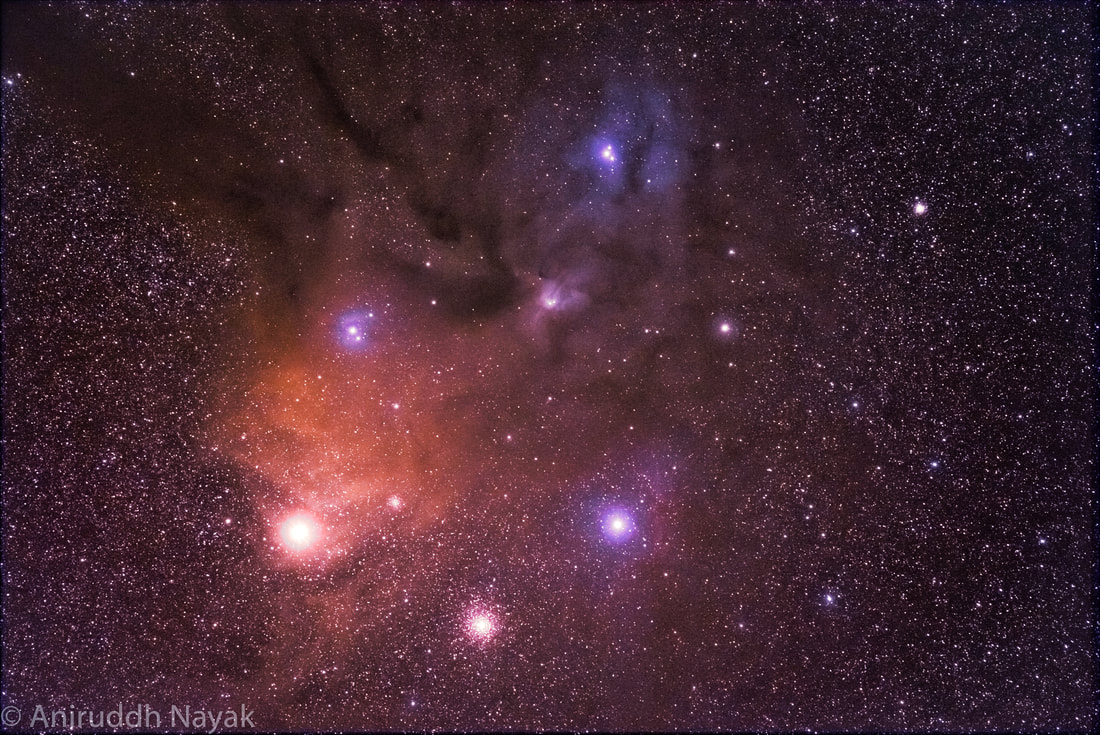
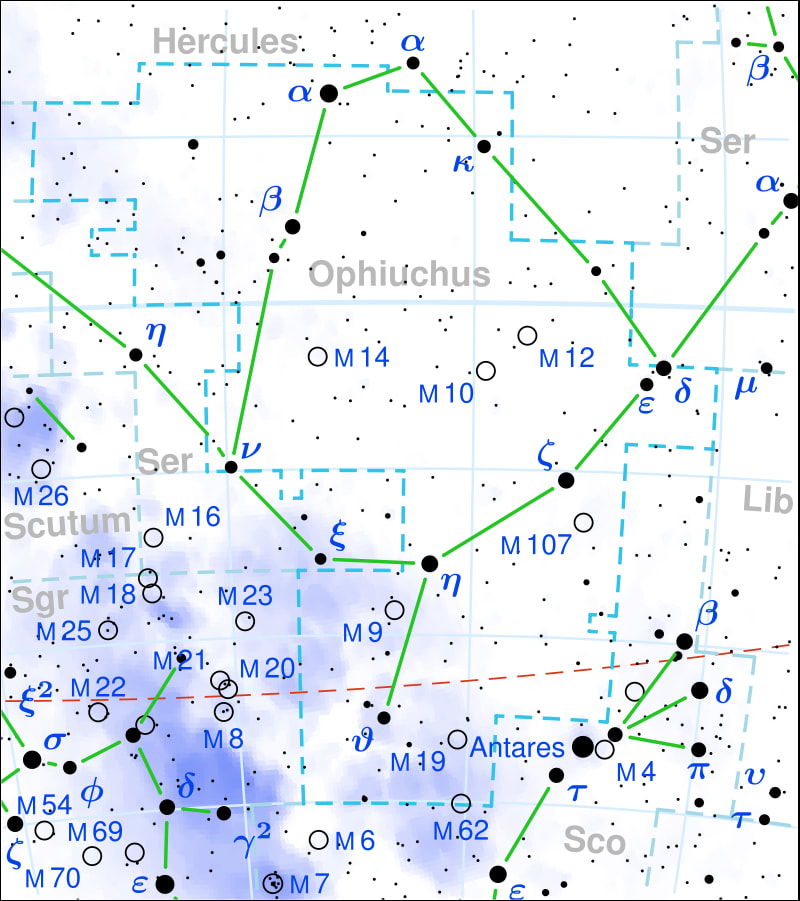
Rho-Ophiushi Star Cluster
Ani said that this photo was a 30-minute exposure taken from his Canon dsir with a 200 mm lens on a star tracking mount.
Rho Ophiuchi (ρ Ophiuchi) is a multiple star system in the constellation Ophiuchus. The central system has an apparent magnitude of 4.63.[2] Based on the central system's parallax of 9.03 mas,[1] it is located about 360 light-years (110 parsecs) away.[1] The other stars in the system are slightly farther away.[11]
The Rho-Ophiushi star cluster is that dot above the bright star Antares in Scorpius but the dot within the border of Ophiuchus closest to the corner. The red-dashed line is the Ecliptic that all the planets orbit close to. It's interesting to me that this star cluster is not a Meiser Object, or NGC object, or IC object.
Other
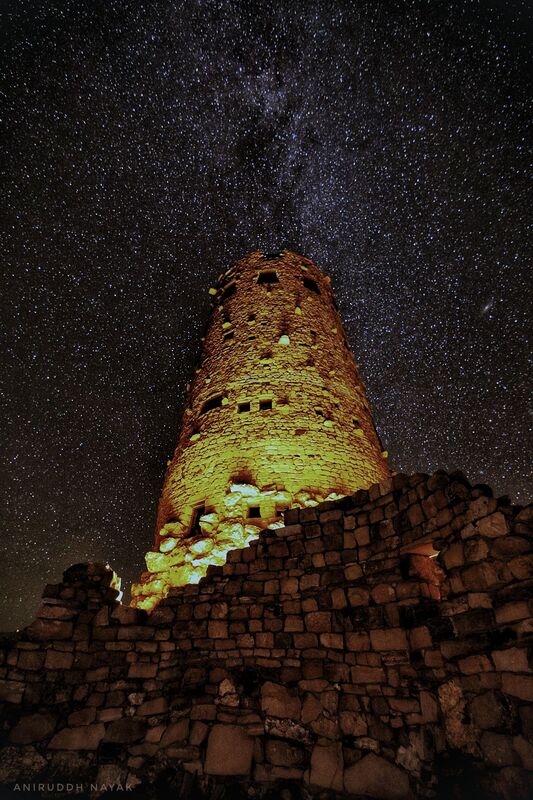
The Grand Canyon Watch Tower
The Desert View Watchtower (1932) dominates the near view. This structure was designed by Mary Elizabeth Jane Colter who is often referred to as the architect of the southwest. She traveled throughout the southwest to find inspiration and authenticity for her buildings. The architecture of the ancestral Puebloan people of the Colorado Plateau served as her model. This particular tower was patterned after those found at Hovenweep and the Round Tower of Mesa Verde. Colter indicated that it was not a copy of any that she had seen, but rather modeled from several.
As you get closer to the building you might see how well it blends into the environment. It is difficult to tell where the rock of the canyon walls end, and the tower begins. She said:
“First and most important, was to design a building that would become part of its surroundings; one that would create no discordant note against the time eroded walls of this promontory.”
To obtain this result she insisted that the rocks not be cut or worked, so they would not lose the “weathered surfaces so essential to blend it with the canyon walls”.
As you get closer to the building you might see how well it blends into the environment. It is difficult to tell where the rock of the canyon walls end, and the tower begins. She said:
“First and most important, was to design a building that would become part of its surroundings; one that would create no discordant note against the time eroded walls of this promontory.”
To obtain this result she insisted that the rocks not be cut or worked, so they would not lose the “weathered surfaces so essential to blend it with the canyon walls”.
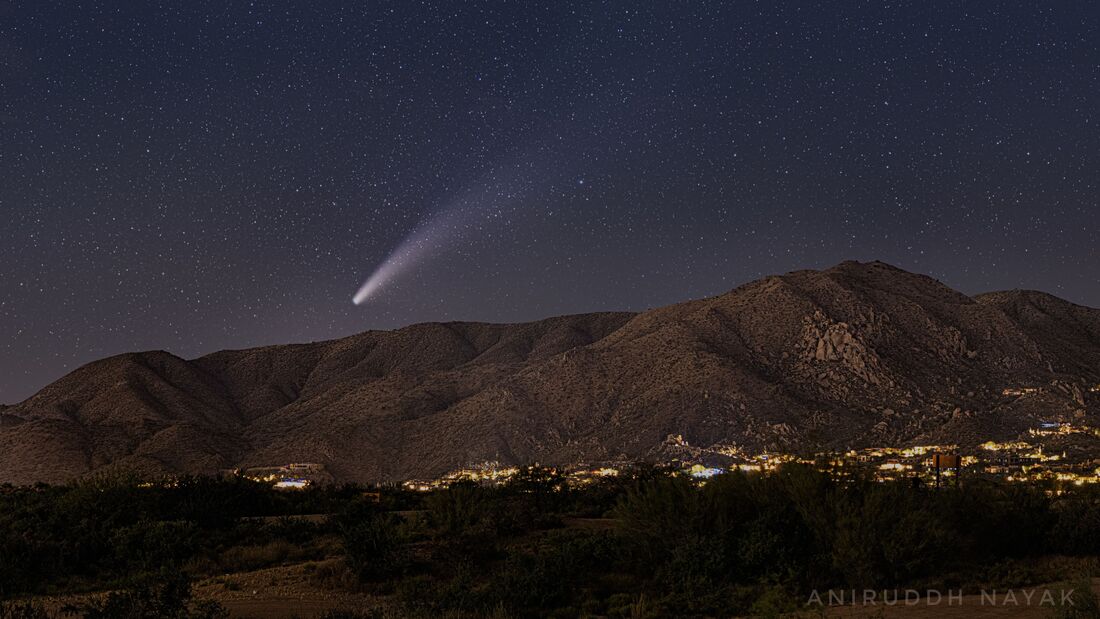
Comet Neowise (2020) Setting Behind the Mountains
Comet Neo-wise was recently discovered on March 27, 2020 and is officially known as "C/2020 F3."
A comet (not to be confused with an asteroid or meteorite) is an icy, rocky object that orbits the Sun. Comets are cosmic snowballs of frozen gases, rock, and dust that orbit the Sun. When frozen, they are the size of a small town. When a comet's orbit brings it close to the Sun, it heats up and spews dust and gases into a giant glowing head larger than most planets. The dust and gases form a tail that stretches away from the Sun for millions of miles. There are likely billions of comets orbiting our Sun in the Kuiper Belt and even more distant Oort Cloud.
The current number of known comets is:
3,743A recent study at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory estimates the comet holds up to 13 million Olympic size swimming pools (about 8,580,000,000,000 gallons of water.)
Neo-wise is about 3 miles in diameter but it's tail takes up 6 degrees in the sky or a dozen Full Moon diameters.
Because of Neo-wise's long estimated orbit, the comet will only be seen again on Earth in 6,800 years.
A comet (not to be confused with an asteroid or meteorite) is an icy, rocky object that orbits the Sun. Comets are cosmic snowballs of frozen gases, rock, and dust that orbit the Sun. When frozen, they are the size of a small town. When a comet's orbit brings it close to the Sun, it heats up and spews dust and gases into a giant glowing head larger than most planets. The dust and gases form a tail that stretches away from the Sun for millions of miles. There are likely billions of comets orbiting our Sun in the Kuiper Belt and even more distant Oort Cloud.
The current number of known comets is:
3,743A recent study at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory estimates the comet holds up to 13 million Olympic size swimming pools (about 8,580,000,000,000 gallons of water.)
Neo-wise is about 3 miles in diameter but it's tail takes up 6 degrees in the sky or a dozen Full Moon diameters.
Because of Neo-wise's long estimated orbit, the comet will only be seen again on Earth in 6,800 years.
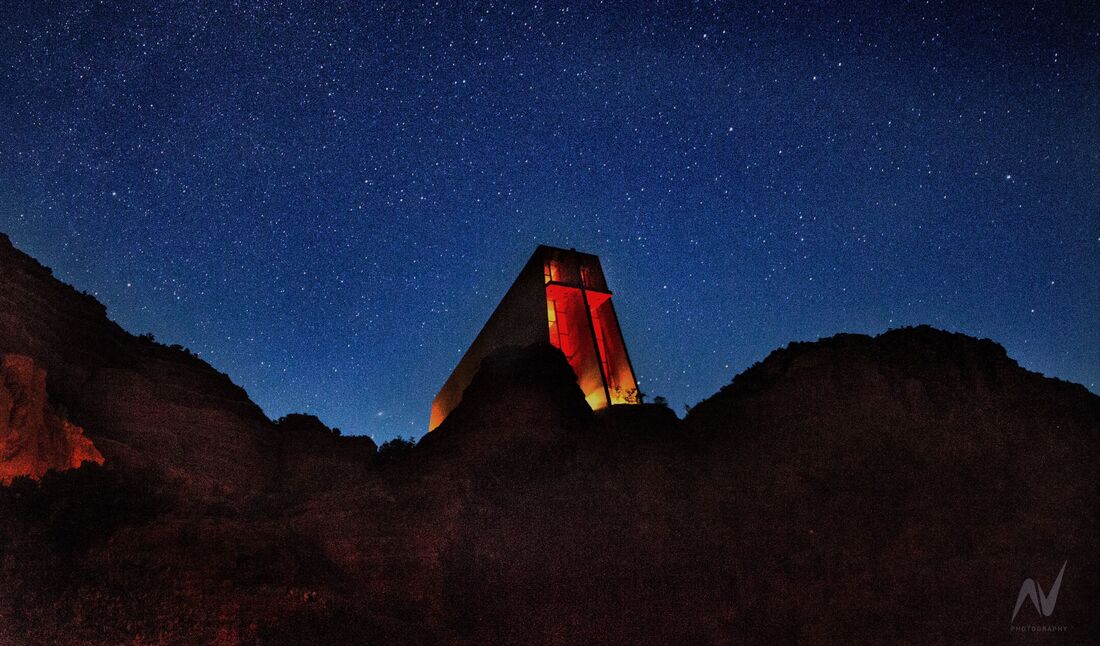
Chapel of the Holy Cross in Sedona, AZ
The Chapel of the Holy Cross has been a fixture of the Sedona community since its completion in 1956. It landed in the buttes of Sedona after its intended place in Budapest, Hungary was not a practical place for construction after World War II. 20 years of planning and design work lead to this incredible feature becoming a part of the Sedona landscape. The Sedona chapel seamlessly flows with the surrounding area, rising out of the red rocks just like a prominent peak. You can find this amazing attraction on the south side of Sedona just east of the 159. You are sure not to miss it.
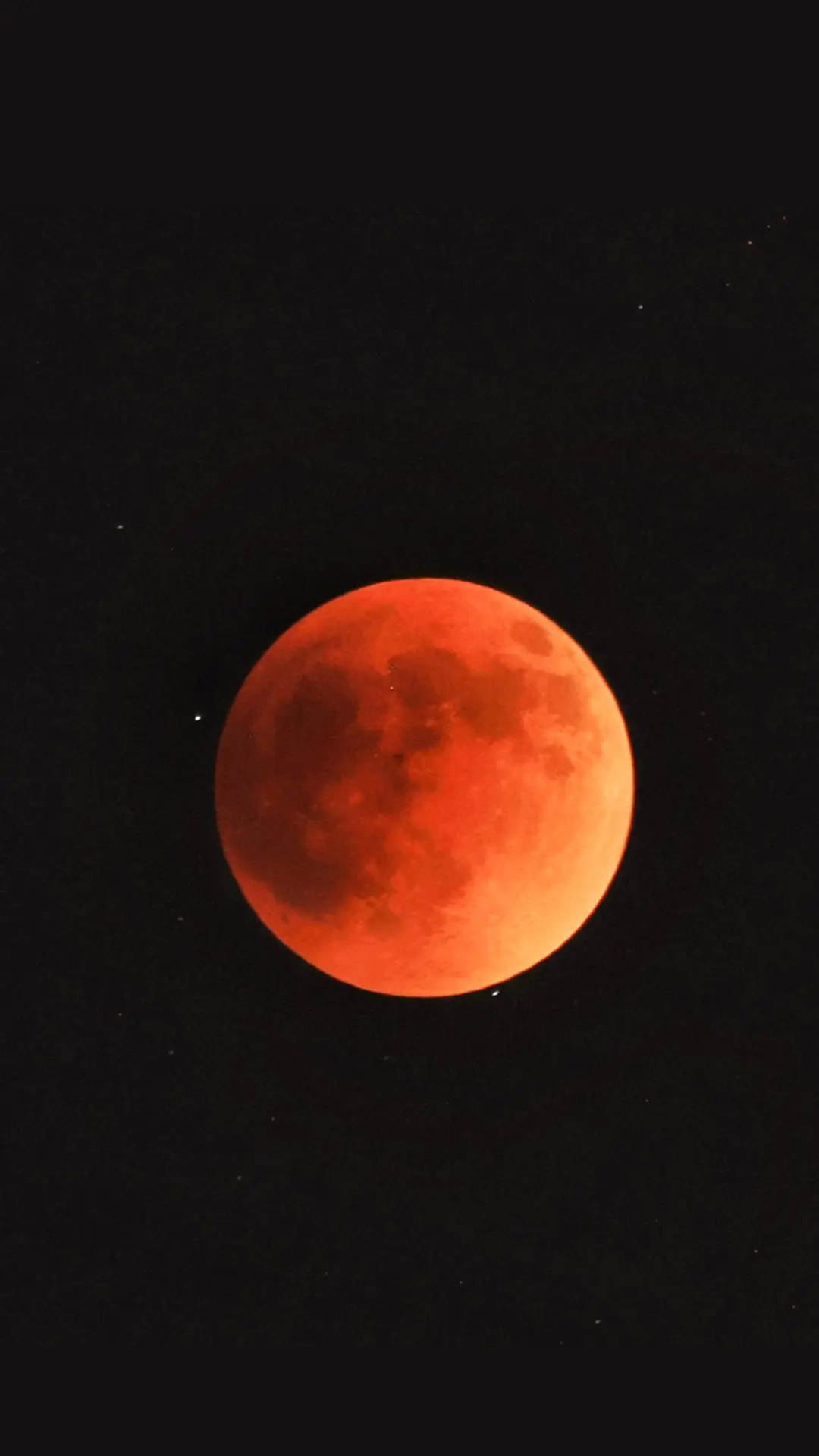
Total Lunar Eclipse
May 15, 2022 from Headwaters in Dripping Springs, TX
May 15, 2022 from Headwaters in Dripping Springs, TX